"Joel’s process taught me to cut out the noise that doesn’t serve me” - Navy SEAL

LEARN HOW TO CONTROL YOUR MIND TO PERFORM
AT YOUR HIGHEST POTENTIAL IN ANY ARENA OF LIFE...
Former SWAT Sniper Reveals the System to Win the Mental Game...


ARE YOU CHOKING WHEN THE PRESSURE RISES?
Everything in life is a mental game...
Swinging a baseball bat is a mental game…
Parenting is a mental game…
Public speaking is a mental game…
We are all playing the mental game several times a day whether we know it or not...

Joel Turner training the Phillies on
how to apply MindIQ to baseball
If you aren't performing at your potential
it’s because you are losing the mental game...
We lose the mental game because our brains aren’t wired to win it. They are hard-wired for survival which means they will seek to avoid anything they perceive as distress.
So, whether you are pitching a baseball or performing a public presentation, the problem lies in where you place your conscious mind...
If your conscious mind is in the wrong place your performance will be crippled...
But there is good news… just like anything in life this is a skill that you can learn & blueprint to control your mind in any arena to succeed at a level you never thought possible!
YOU MUST LEARN TO PLAY & WIN THE MENTAL GAME.


INTRODUCING...

THE MENTAL GAME BLUEPRINT BEHIND MAJOR LEAGUE
BASEBALL TEAMS, SWAT SNIPERS, AND HIGH-PERFORMERS
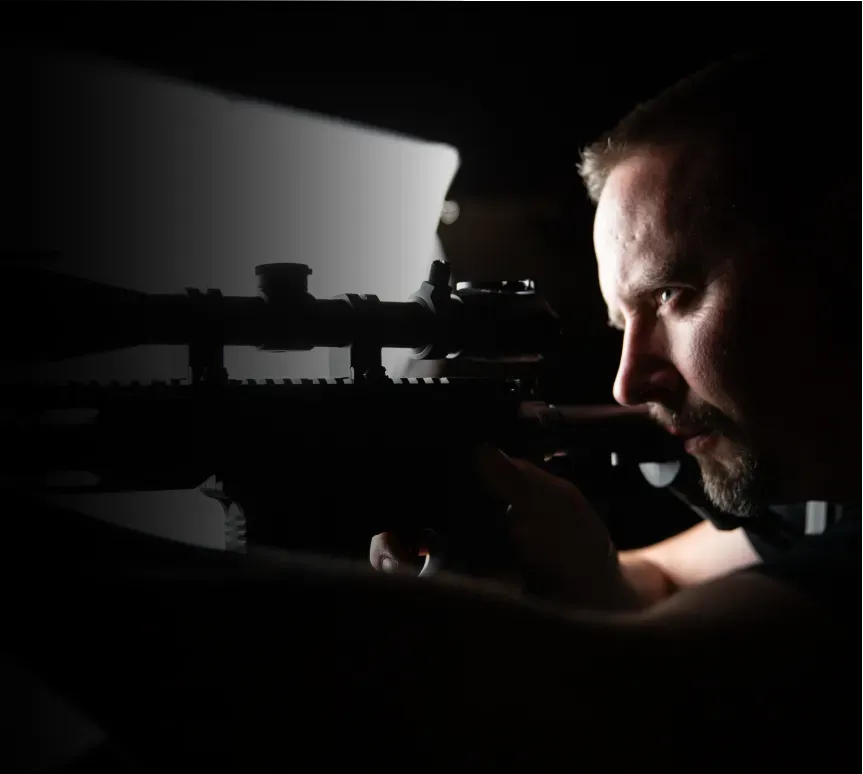

MEET YOUR COACH
JOEL TURNER
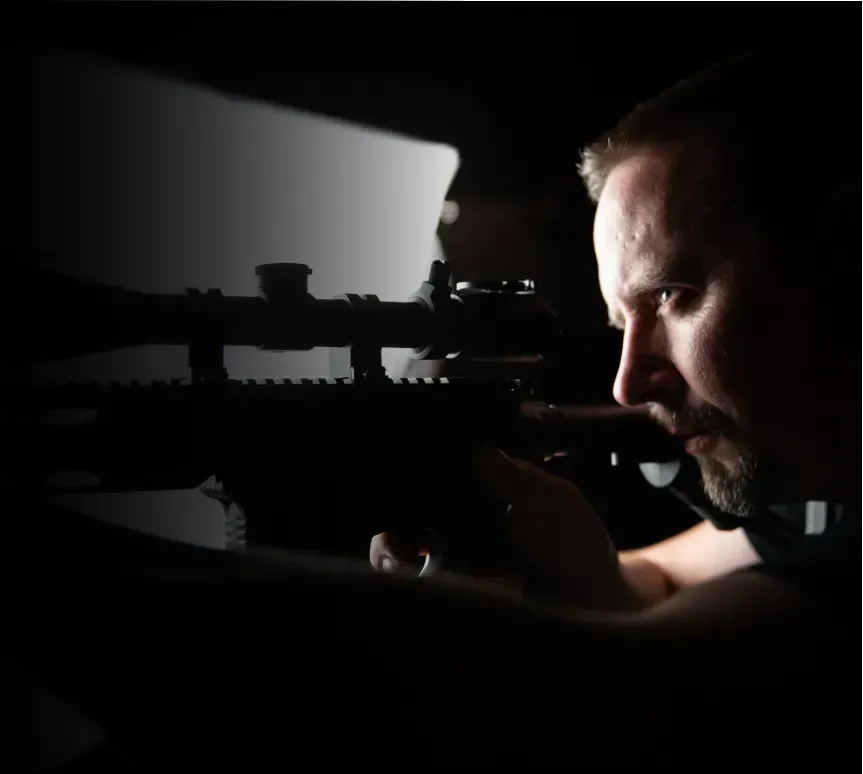

With experiences ranging from a SWAT sniper
to coaching Major League Baseball teams,
Joel's teachings aren't hypothetical. They're born from high-stakes situations and refined through rigorous scientific inquiry.
When you learn from Joel, you're receiving insights forged in the fires of real-world challenges.
With experiences ranging from a SWAT sniper to coaching Major League Baseball teams, Joel's teachings aren't hypothetical. They're born from high-stakes situations and refined through rigorous scientific inquiry.
When you learn from Joel, you're receiving insights forged in the fires of real-world challenges.
SYSTEMS forged through life or death stakes...
How did I learn to win the mental game?
I struggled with it myself for many years. As a S.W.A.T. Sniper, I faced life or death decisions that drove me into the world of neuroscience and psychological studies...
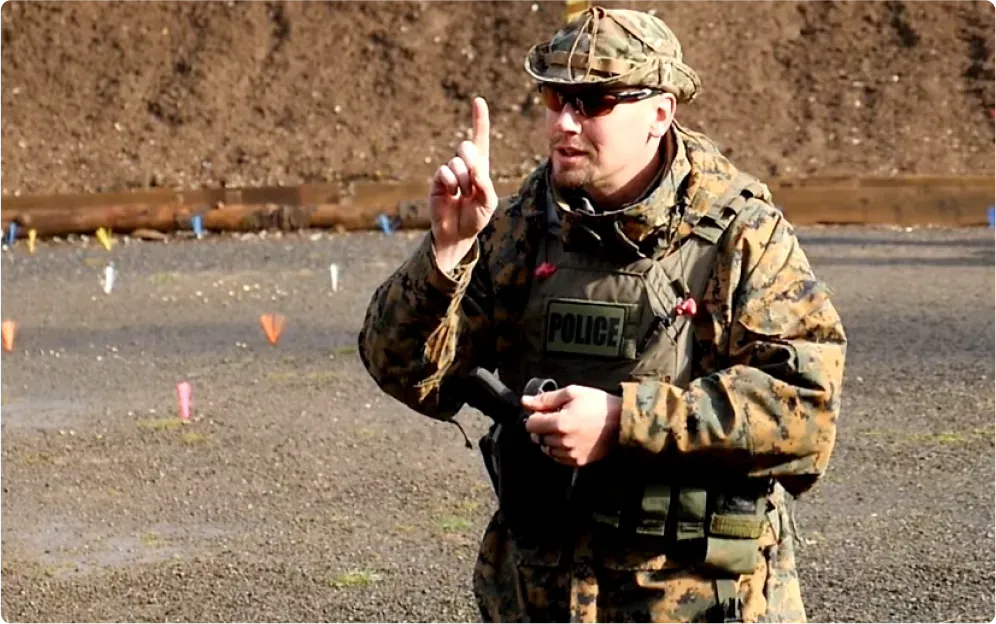

I worried if I'd be able to perform when it mattered most...
But, S.W.A.T. wasn’t the only practice I got in the mental game.
My desire to learn how to control my mind was escalated from my experience as a bowhunter...
I struggled with “target panic” - an archers nemesis where the body’s fight-or-flight response takes over...
The high-stress reactions I faced as a an archer mirrored what I felt in my role as a sniper.
It didn’t matter how much I practiced. When the pressure increased my accuracy plummeted.
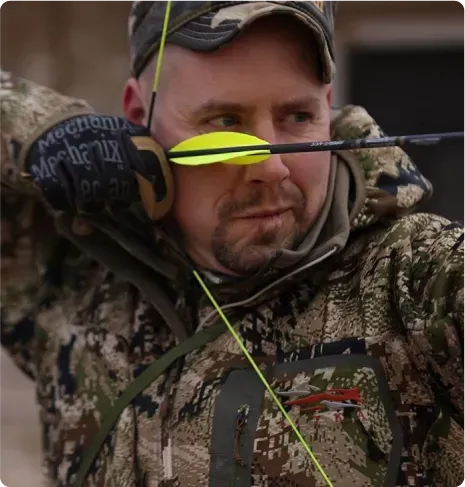

I knew I needed to master my own responses to the intense stressors of my job...
This personal battle sent me into a deep dive of the human nervous system, visual proprioception, and motor programming. My quest for knowledge transformed my struggles into strategies that increased my performance...
After applying these strategies personally, I became the lead firearms instructor for the state of Washington where I taught hundreds of law enforcement officers the mental game of shooting...
Eventually, I launched ShotIQ, where we’ve trained thousands of archers how to control their mind in high stress events...
These students were finally able to perform no matter the stakes.
But, there was still one big problem. This system only applied to shooting...
A suggestion from Joe Rogan started it all...
In 2023, Joe Rogan invited me on his podcast to discuss archery and how it applies to life...
On that podcast Joe said, “I think that what you teach applies to life, it applies to anxiety filled situations...”
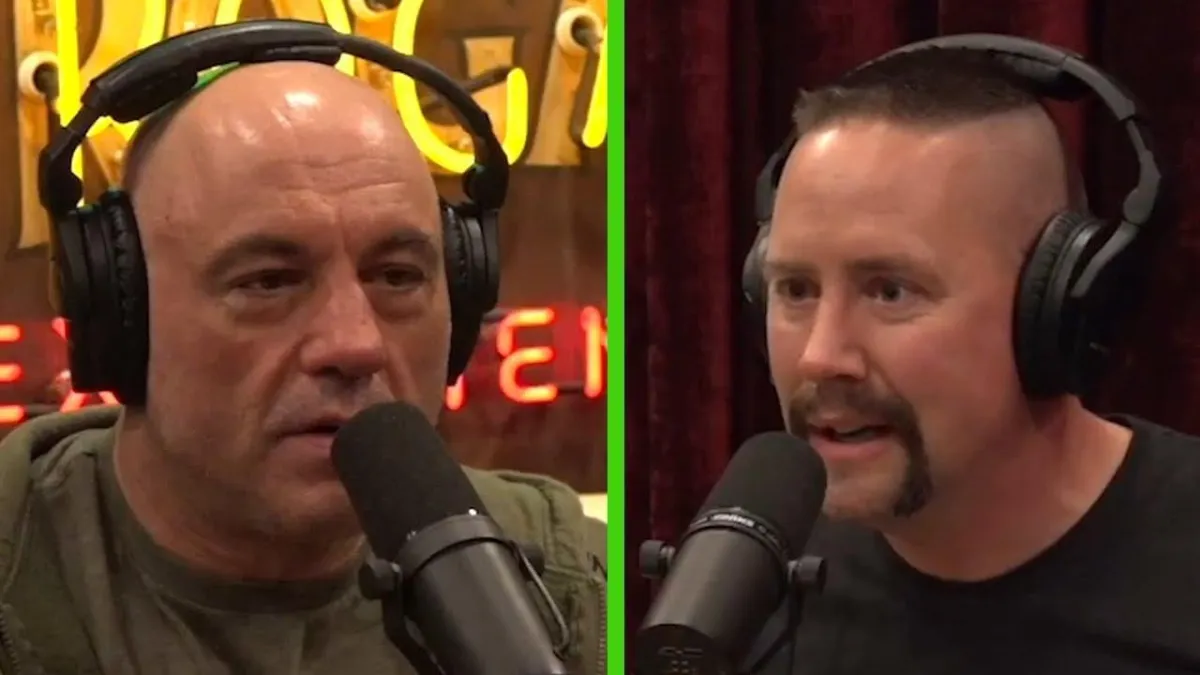
And in came pouring in the emails from surgeons, sports players, and special operation teams wanting to talk to me about applying my system to their field.
I recognized the universal application of my discoveries, I began to refine my approach to master the mental game to excel in any high-pressure environment.
After rigorous research, I launched The Turner Model, teaching this model to high performers ranging from professional sports teams, special operators, and first responders...
The Turner Model teaches how to override the subconscious's automatic fight- or-flight response, enabling individuals to remain composed and focused, transforming high-pressure challenges into stellar performances...
THE EQUATION TO
OVERCOME YOUR MIND
Simply plug your problem into The Mental Game Equation:
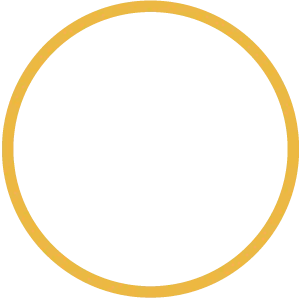
DEFINE
Define when the moment of
truth is, and where conscious control must exist.
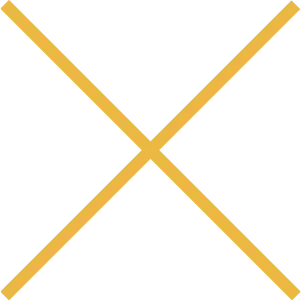
OVERRIDE
Make a decision to override
your thoughts and your
nervous system.
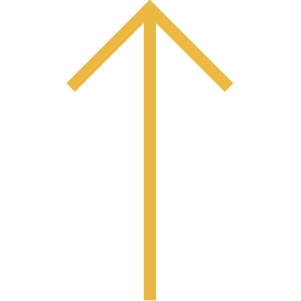
EXECUTE
Use self-instruction (speech)
to guide yourself through the moment of truth.
TAUGHT EXCLUISVELY IN


My Life’s Mental Games
From being a S.W.A.T Sniper, hunter, and now public speaker Joel takes you through the mental games he’s had to play in his life and how he’s consistently won.


Thoughts Aren’t Thinking
You must know the difference between thoughts and thinking before you can ever play a mental game. Thoughts are what you hear, thinking is what you say. You will learn the power of your own voice and how it relates to overriding thoughts.


The Signature Test
This test will show you the difference between open and closed loop control systems in the mind. You must know the difference between open and closed loop control systems before you could ever fix a movement problem.


Open & Closed Loop Systems
Knowing the difference between and closed loop will allow you to diagnose the Where and the When of the mental game equation. When you understand open and closed loop control systems, you will understand how to fix a movement and when a movement can actually be fixed within a process.


Adult Learning Model
The adult learning model starts with the cognitive stage of learning, moves to the practice stage of learning, with the goal of landing in the automatic stage of learning. The problem is, when we reach the automatic stage, we may have built incorrect motor programs that will plague our movement quality and effectiveness. We must know how to get back to the cognitive stage of learning to fix a problem.


The Mental Game Equation
How can you possible win a game where you don’t know when the game starts, you don’t know the rules of the game, and you don’t know who your opponents are? The mental game equation defines the rules of the game, when the game must be played, and how to win the game. The code to winning the mental game has finally been cracked with the Mental Game Equation.


Fixing Movement Problems
To fix a movement problem, you must understand the fact that Thoughts are not Thinking, open and closed loop control systems, the Mental Game Equation, and finally Blueprinting. Movement problems become easy to fix when you are able to laser focus your conscious mind into the root of the problem.


Fixing Cerebral Problems
Cerebral problems like an anxiety attack or a parenting issue can be tricky. However, when you have the mental game equation, these problems have some very simple solutions. You must regain your perspective. You must regain your presence. This course will show you HOW to do just that.


Application: Mental Game Equation
When you understand the equation, you now have the power to plug in life’s problems into the equation. This will allow you to understand the mental game of the solution. The solutions to the problems will no longer be a mystery. You will finally understand how you do what you do.


Blueprinting
If success is a mystery, then failure is a mystery. If you don’t know how you do what you do, you are leaving your success to chance. Understanding how to blueprint a solution is a very powerful feeling. When you know how you did something, and you blueprint it, you can now use that something to make you blueprint stronger every time you do it. Success will no longer be a mystery. Failure will no longer be a mystery so it will be turned into success.

And more including...

Fixing Problems in Golf
Golf has a unique set of common movement problems. Joel diagnoses those problems and applies the mental game equation to help produce consistent results in your swing.


Fixing Problems in Baseball
After coaching the Philadelphia Phillies they set records never attained in the MLB. Joel since cemented the application of his system into baseball. In this section, Joel will train you on how to apply the mental game equation to pitching.


Fixing Problems in Basketball
Basketball was one of the first sports that the MindIQ methods were proven on. Joel trained a local basketball team on these methods and they quickly began to break records. Now, Joel is sharing the system for fixing problems in Basketball in this course.

WHAT IS THE INVESTMENT?
CLICK “SIGN UP NOW” TO GET INSTANT DIGITAL ACCESS
$247
WHAT YOU GET WHEN YOU JOIN MINDIQ
25+ MODULES OF STEP-BY-STEP TRAINING
GUIDANCE FROM LEADING EXPERT JOEL TURNER
24/7 MINDIQ CUSTOMER SUPPORT
LIFETIME ACCESS & FREE UPDATES FOR LIFE
ALL-NEW TRAINING FROM JOEL FOR 2024
WHAT THE
EXPERTS ARE SAYING

"...What Joel has taught me, in a very short period of time, is how to control my mind in such situations that it can focus on something other than recoil, thereby giving the best chance of hitting my target, every time."
- Dr. Peter Attia
@peterattiamd

“I think that what you teach applies to life, it applies to anxiety filled situations... You have figured out something that is so useful, so repeatable, and so important.”
- Joe Rogan
@JoeRogan

“Originally, I went to see Joel to improve my archery skills. I shortly realized I could apply his technique to many other aspects of life, including controlling my TBI and PTSD symptoms. Joel’s process taught me to cut out the noise that doesn’t serve me and bring my focus back to the task at hand”
- John Cizin
Former Navy Seal

"...I use his process daily with our pitchers to blueprint success and learn from mistakes. Stadiums get loud and we are working to be the loudest in the room thanks to Joel.
One shot, one pitch at a time."
- Caleb Cotham
Phillies Head Pitching Coach

"The Turner Model, specifically ShotIQ, has taken my archery skills to a whole new level.” I’ve always known a sharp mental edge was the key in high-stakes situations. The Model has provided me with the tools to excel in those moments.”
- Donnie Vincent
@Donnie_Vincent
CLICK “SIGN UP NOW” TO GET INSTANT DIGITAL ACCESS
$247
WHAT YOU GET WHEN YOU JOIN MINDIQ
25+ MODULES OF STEP-BY-STEP TRAINING
GUIDANCE FROM LEADING EXPERT JOEL TURNER
24/7 MINDIQ CUSTOMER SUPPORT
LIFETIME ACCESS & FREE UPDATES FOR LIFE
ALL-NEW TRAINING FROM JOEL FOR 2024
OUR METHODS ARE PROVEN



"We were fortunate to have Joel visit Spring Training and speak with our pitching staff and coaches. Pitching at it's core is making precise decisions on what and where to throw pitches.
We have more control over this than where the balls ends up. He de-mystified the process for being good at the "mental game" of pitching. I use his process daily with our pitchers to blueprint success and learn from mistakes. Stadiums get loud and we are working to be the loudest in the room thanks to Joel. One shot, one pitch at a time."
- Caleb Cotham | Phillies Head Pitching Coach
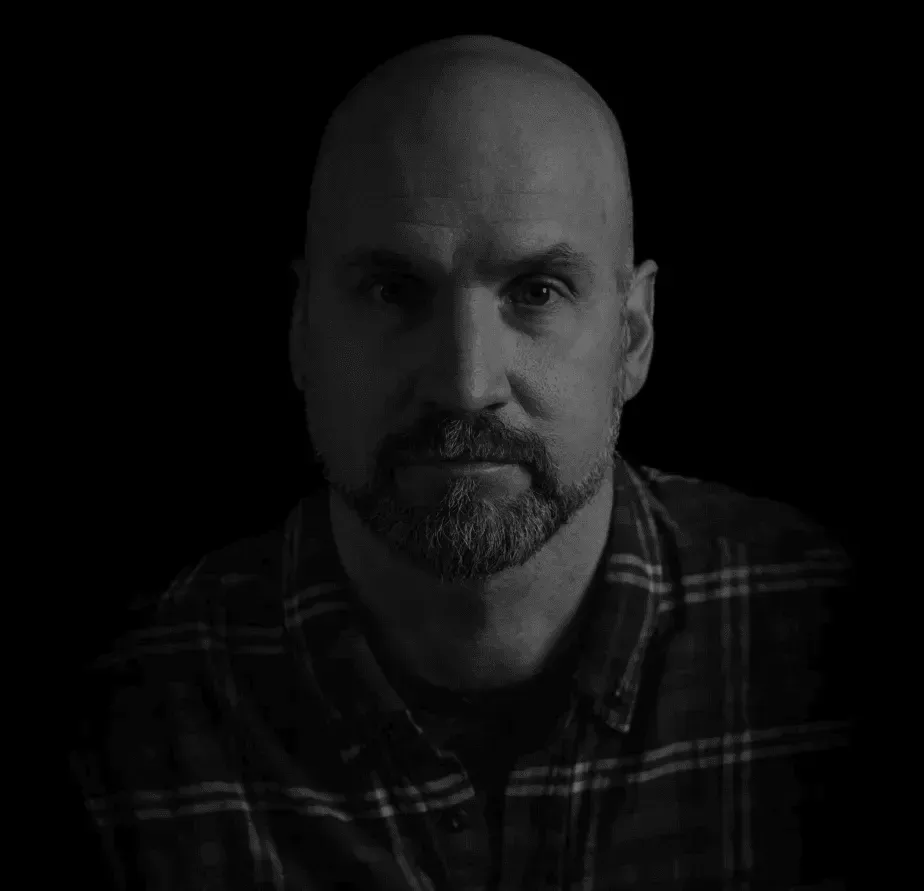


"After a near decades worth of use, I can wholeheartedly say that this model is reliable, and applicable to so much more than just shooting.
I have incorporated this into just about every aspect of my life.”
- Dr. Dan Gilday
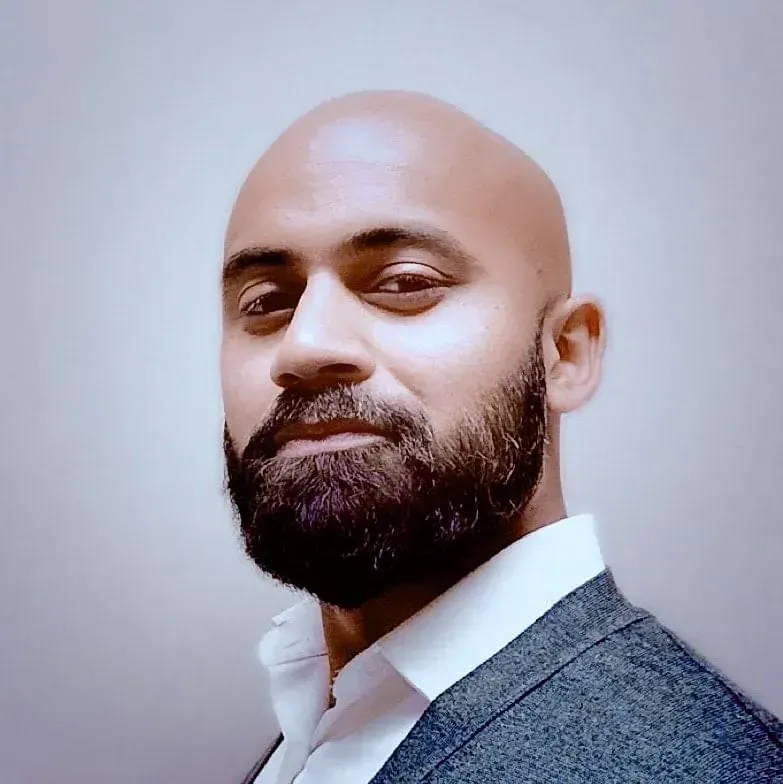

"When I met Joel, ShotIQ significantly elevated my archery, but it is MindIQ that has completely transformed my life. MindIQ is ShotIQ applied to every arena and aspect of life.
Becoming the ultimate problem solver is a great gift, but even greater is seeing the power of teaching this skill to my children and witnessing the incredible impact it's had on my marriage, my business, and my physical and mental health.”
- Dylan Drego | @dylan.drego
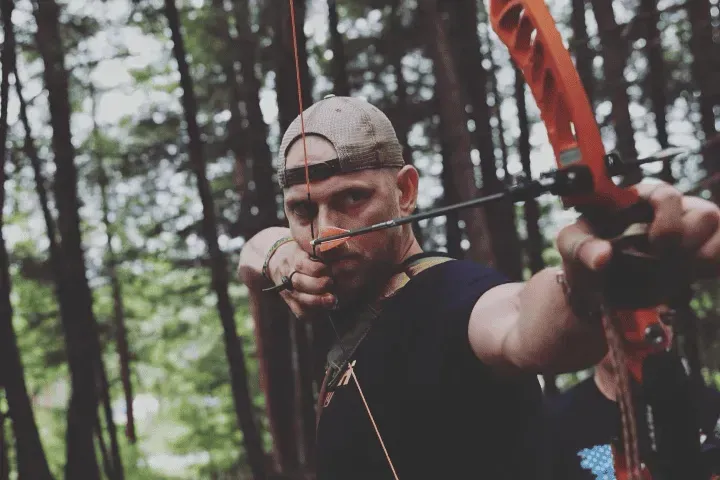


"I’ve been a long time student of Joel’s in the archery and precision shooting arena. His instruction has been nothing less than transformational for my mental game. Joel’s understanding of the mind and how to control it in the moment of truth has helped thousands of shooters around the globe unlock their full potential.
Joel’s entrance into the sports movement arena will be the greatest gift to sports in the last few decades. Joel’s practical application of the science of the mind to sports and day to day cerebral problems is sure to unlock the full potential of performance in all arenas of the human experience. Whether you’re an amateur hobbyist or an elite level professional in your craft, I can’t recommend MindIQ enough."
- Matt Zirnsak | The Push Archery
CLICK “SIGN UP NOW” TO GET INSTANT DIGITAL ACCESS
$247
WHAT YOU GET WHEN YOU JOIN MINDIQ
25+ MODULES OF STEP-BY-STEP TRAINING
GUIDANCE FROM LEADING EXPERT JOEL TURNER
24/7 MINDIQ CUSTOMER SUPPORT
LIFETIME ACCESS & FREE UPDATES FOR LIFE
ALL-NEW TRAINING FROM JOEL FOR 2024
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS:
-
Q: What is the Turner Model?
The Turner Model is a mental framework for understanding and amplifying concentration, accuracy, and performance.
-
Q: Who is this course for?
This course is for anyone looking to sharpen their mental edge, whether they are professionals, athletes, or someone interested in personal growth.
-
Q: What will I learn in this course?
You'll learn the principles of the Turner Model, the mind-body connection that enables you to override your body's automatic responses in high-stress situations, how to blueprint any situation for success, and practical exercises to train your mind to control any outcome, no matter the stakes.
-
Q: Is prior experience or knowledge required?
No, this course is universally applicable, whether you're just starting to play the mental game or you're ready to master it.
-
Q: What kinds of benefits will I get from this course?
You'll learn to channel your focus, control the outcome of your performance under stress, make better decisions, strengthen your determination, and win more.
-
Q: How is the course structured?
The course is divided into several key modules, each focusing on different aspects of the Turner Model and its applications.
-
Q: Why is the instructor the best messenger for this?
The instructor has not only conceptualized the Turner Model but has applied it in various high-stakes scenarios, including as a SWAT sniper, lending credibility and practical wisdom to the teachings.
-
Q: Does the instructor have real-world experience using the Turner Model?
Yes, the Turner Model has been applied in a variety of professional and personal scenarios, which will be shared throughout the course.
-
Q: How can I apply the Turner Model in my daily life?
The course includes a dedicated module on implementing the Turner Model in everyday situations, making the teachings highly applicable.
-
Q: Does the Turner Model only work in high-stress situations?
In this course, we specifically address how the Model can be effective in both life-and-death situations and everyday scenarios.
-
Q: How do I access the course material?
After purchasing the course, you will be given a unique login to access all course materials online.
-
Q: Is there a time limit to complete the course?
No, you can go through the course at your own pace and will have lifetime access, allowing you to revisit the teachings as often as you'd like.


DON’T WAIT
LEARN HOW TO WIN THE MENTAL GAME FOR THE REST OF YOUR LIFE, TODAY.

Copyright © 2025 Turner Model® | Privacy | Terms | Login
Have a question? Email us at [email protected]
